引言
C++的项目,字符编码是一个大坑,不同平台之间的编码往往不一样,如果不同编码格式用一套字符读取格式读取就会出现乱码。因此,一般都是转化成UTF-8这种平台通用,且支持性很好的编码格式。
字符编码知识
先简单介绍一下Unicode、UTF-8、ANSI之间的概念。
- GB2312/BIG5:中国制定的编码规范
GB2312: 简体中文
BIG5: 繁体中文
GBK: 亚洲双字节字符统一的编码格式,兼容所有平台
下面通过Post not found: C-检测字符编码 C-检测字符编码中提到的在线查字符编码,得到下表
| 字符 |
GB2312 |
Unicode |
UTF-8 |
GBK |
| 中 |
D6D0 |
00004E2D |
E4B8AD |
D6D0 |
| H |
48 |
00000048 |
48 |
48 |
字符编码转化
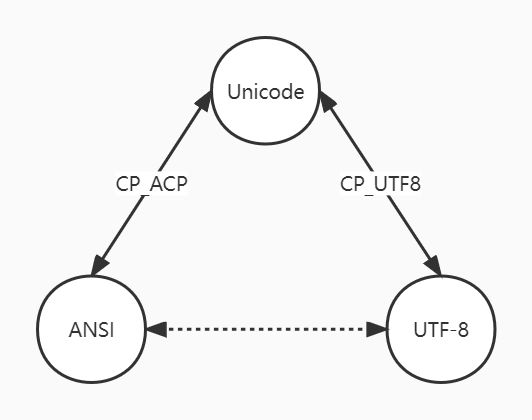
由于Unicode能表示所有的字符和符号,因为是字符编码转化的桥梁,所以能做到在Unicode、UTF-8、ANSI这三种编码格式中自由转换,如下图所示:

在Windows平台下,可以通过标准库或则是windows的API。
C++11对国际化标准做得还是可以的,提供了这些接口,标准库没有提供UTF-8到ANSI的互相转化接口,需要自行封装。
ANSI、UTF-8、Unicode三者之间的转换主要依赖于WideCharToMultiByte和MultiByteToWideChar两个函数。
Windows API函数拥有“A”和“W”版本,“A”版本基于Windows Code Page,而“W”版本则基于Unicode字符。
所以windows用“W”版本是明智的选择
- Unicode转UFT-8:设置
WideCharToMultiByte的CodePage参数为CP_UTF8;
- UTF-8转Unicode:设置
MultiByteToWideChar的CodePage参数为CP_UTF8
- Unicode转ANSI:设置
WideCharToMultiByte的CodePage参数为CP_ACP;
- ANSI转Unicode:设置
MultiByteToWideChar的CodePage参数为CP_ACP;
- UTF-8转ANSI:先将UTF-8转换为Unicode,再将Unicode转换成ANSI;
- ANSI转UTF-8:先将ANSI转换为Unciode,再将Unicode转换成ANSI。
Unicode、ANSI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| std::string UnicodeToAnsi(const std::wstring & wstr)
{
std::string ret;
std::mbstate_t state = {};
const wchar_t *src = wstr.data();
size_t len = std::wcsrtombs(nullptr, &src, 0, &state);
if (static_cast<size_t>(-1) != len) {
std::unique_ptr< char [] > buff(new char[len + 1]);
len = std::wcsrtombs(buff.get(), &src, len, &state);
if (static_cast<size_t>(-1) != len) {
ret.assign(buff.get(), len);
}
}
return ret;
}
std::wstring AnsiToUnicode(const std::string & str)
{
std::wstring ret;
std::mbstate_t state = {};
const char *src = str.data();
size_t len = std::mbsrtowcs(nullptr, &src, 0, &state);
if (static_cast<size_t>(-1) != len) {
std::unique_ptr< wchar_t [] > buff(new wchar_t[len + 1]);
len = std::mbsrtowcs(buff.get(), &src, len, &state);
if (static_cast<size_t>(-1) != len) {
ret.assign(buff.get(), len);
}
}
return ret;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| std::wstring AnsiToUnicode(const std::string &strAnsi)
{
int nUnicodeLen = ::MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP,
0,
strAnsi.c_str(),
-1,
NULL,
0);
wchar_t* pUnicode = new wchar_t[nUnicodeLen + 1];
memset((void*)pUnicode, 0, (nUnicodeLen + 1) * sizeof(wchar_t));
::MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP,
0,
strAnsi.c_str(),
-1,
(LPWSTR)pUnicode,
nUnicodeLen);
std::wstring strUnicode;
strUnicode = (wchar_t*)pUnicode;
delete[]pUnicode;
return strUnicode;
}
std::string UnicodeToAnsi(const std::wstring& strUnicode)
{
int nAnsiLen = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,
0,
strUnicode.c_str(),
-1,
NULL,
0,
NULL,
NULL);
char *pAnsi = new char[nAnsiLen + 1];
memset((void*)pAnsi, 0, (nAnsiLen + 1) * sizeof(char));
::WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,
0,
strUnicode.c_str(),
-1,
pAnsi,
nAnsiLen,
NULL,
NULL);
std::string strAnsi;
strAnsi = pAnsi;
delete[]pAnsi;
return strAnsi;
}
|
UTF-8、Unicode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| std::string UnicodeToUtf8(const std::wstring & wstr)
{
std::string ret;
try {
std::wstring_convert< std::codecvt_utf8<wchar_t> > wcv;
ret = wcv.to_bytes(wstr);
} catch (const std::exception & e) {
std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return ret;
}
std::wstring Utf8ToUnicode(const std::string & str)
{
std::wstring ret;
try {
std::wstring_convert< std::codecvt_utf8<wchar_t> > wcv;
ret = wcv.from_bytes(str);
} catch (const std::exception & e) {
std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return ret;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| std::wstring Utf8ToUnicode(const std::string& str)
{
int nUnicodeLen = ::MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8,
0,
str.c_str(),
-1,
NULL,
0);
wchar_t* pUnicode;
pUnicode = new wchar_t[nUnicodeLen + 1];
memset((void*)pUnicode, 0, (nUnicodeLen + 1) * sizeof(wchar_t));
::MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8,
0,
str.c_str(),
-1,
(LPWSTR)pUnicode,
nUnicodeLen);
std::wstring strUnicode;
strUnicode = (wchar_t*)pUnicode;
delete []pUnicode;
return strUnicode;
}
std::string UnicodeToUtf8(const std::wstring& strUnicode)
{
int nUtf8Length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8,
0,
strUnicode.c_str(),
-1,
NULL,
0,
NULL,
NULL);
char* pUtf8 = new char[nUtf8Length + 1];
memset((void*)pUtf8, 0, sizeof(char) * (nUtf8Length + 1));
::WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8,
0,
strUnicode.c_str(),
-1,
pUtf8,
nUtf8Length,
NULL,
NULL);
std::string strUtf8;
strUtf8 = pUtf8;
delete[] pUtf8;
return strUtf8;
}
|
UTF8、ANSI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| std::string AnsiToUtf8(const std::string &strAnsi)
{
std::wstring strUnicode = AnsiToUnicode(strAnsi);
return UnicodeToUTF8(strUnicode);
}
std::string Utf8ToAnsi(const std::string &strUtf8)
{
std::wstring strUnicode = UTF8ToUnicode(strUtf8);
return UnicodeToANSI(strUnicode);
}
|
参考
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/c23f3ea5443d
- https://blog.csdn.net/bladeandmaster88/article/details/54849660
- https://blog.csdn.net/bajianxiaofendui/article/details/83302855
- https://blog.csdn.net/Fengfgg/article/details/115539849